Reading material for Lesson 2.1 Educational Psychology and Teaching
6. Teaching / Training
6.1. Teaching / Training skills
Teaching/training is a complex multifaceted activity, often requiring an instructor to juggle multiple tasks and goals simultaneously and flexibly. The following set of principles can make teaching both more effective and efficient by helping us create the conditions support trainee learning. While implementing these principles requires a commitment in time and effort, it often saves time and energy later on.
Effective teaching involves acquiring relevant knowledge about trainees and using that knowledge to inform our course design and classroom teaching/ training.
When we teach/train, we do not just teach the content, we teach learners the content. A variety of learners characteristics can affect learning. For example, learners cultural and generational backgrounds influence how they see the world; disciplinary backgrounds lead learners to approach problems in different ways; and learners prior knowledge (both accurate and inaccurate aspects) shapes new learning.
Effective teaching involves aligning the three major components of instruction: learning objectives, assessments, and instructional activities.
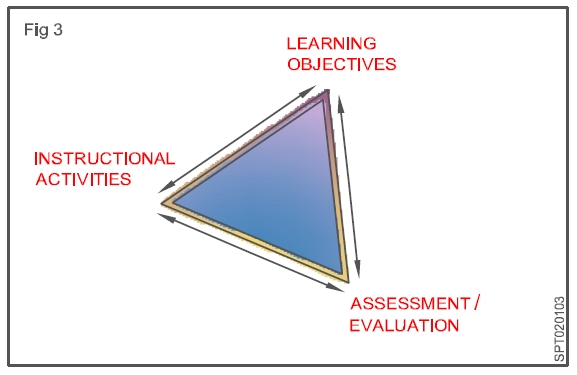
Teaching is more effective and learner learning is enhanced when (a) we, as instructors, articulate a clear set of learning objectives (i.e., the knowledge and skills that we expect learners to demonstrate by the end of a course); (b) the instructional activities (e.g., case studies, labs, discussions, readings) support these learning objectives by providing goal-oriented practice; and (c) the assessments (e.g., tests, papers, problem sets, performances) provide opportunities for learners to demonstrate and practice the knowledge and skills articulated in the objectives, and for instructors to offer targeted feedback that can guide further learning.
Effective teaching involves articulating explicit expectations regarding learning objectives and policies.
Trainer being clear about our expectations and communicating them explicitly helps learners learn more and perform better. Articulating our learning objectives (i.e., the knowledge and skills that we expect learners to demonstrate by the end of a course) gives learners a clear target to aim for and enables them to monitor their progress along the way.
Effective teaching involves prioritizing the knowledge and skills we choose to focus on.
Don’t try to do too much in a single course. Too many topics work against learner learning, so it is necessary for us to make decisions – sometimes difficult ones – about what we will and will not include in a course. This involves (a) recognizing the parameters of the course (e.g., class size, learner’s backgrounds and experiences, course position in the curriculum sequence, number of course units), (b) setting our priorities for learner learning, and (c) determining a set of objectives that can be reasonably accomplished.
Effective teaching involves recognizing and overcoming our expert blind spots.
As experts, we tend to access and apply knowledge automatically and unconsciously (e.g., make connections, draw on relevant bodies of knowledge, and choose appropriate strategies) and so we often skip or combine critical steps when we teach.Learners on the other hand, don’t yet have sufficient background and experience to make these leaps and can become confused, draw incorrect conclusions, or fail to develop important skills. They need instructors to break tasks into component steps, explain connections explicitly, and model processes in detail. Though it is difficult for experts to do this, we need to identify and explicitly communicate to learners the knowledge and skills we take for granted, so that learners can see expert thinking in action and practice applying it themselves.
Effective teaching involves adopting appropriate teaching roles to support our learning goals.
We can take on a variety of roles in our teaching (e.g., synthesizer, moderator, challenger, commentator). These roles should be chosen in service of the learning objectives and in support of the instructional activities.
Effective teaching involves progressively refining our courses based on reflection and feedback.
Teaching requires adapting. We need to continually reflect on our teaching and be ready to make changes when appropriate. Knowing what and how to change requires us to examine relevant information on our own teaching effectiveness. We might modify the learning objectives, content, structure, or format of a course, or otherwise adjust our teaching.