Reading material for Lesson 2.3 Laws of Learning and Theories of Learning
4. Theories of learning
4.3. Insight Learning Theory
 |
Kohler Wolfgang Kohler |
|---|
Kohler was one of the founders of Gestalt psychology along with Max Werheimer and Kurt Koffka. He is also famous for his description of insight learning which he tested on animals, particularly chimpanzees. The results of his experiments during the period 1913-1917 were published in German.
When we solve a problem completely, we experience a pleasant feeling called by Kohler the - "AHA Experience". We say as, we suddenly see the answer to the problem. To illustrate the insight learning, observe the following series of numbers. Which number should follow the sequence- 1491625?. If you cannot solve the problem then come back to the problem. Try different arrangement or perceptual organization of the numbers. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5... or odd numbers or even numbers or 12, 22, 32, etc. If you solve the problem you will have a pleasant experience that is AHA Experience!. Note that your solution came suddenly after some time, which you tried, various strategies. Perceptual arrangements helped a great deal. The solution ones you have it can be generalized rather easily or other similar number of problems. These are the characteristics of insight learning.
Insight Learning Theory Experiment:
How insight learning occurs? The cognitive answer to the question is the insight involves a perceptual re- organization of elements in the environment. Kohler worked out a number of insight experiments on chimpanzees and summarized the findings.
Kohler employed
five types of problems to study how the
chimpanzees solve complex
problems. The two most fascinating and important
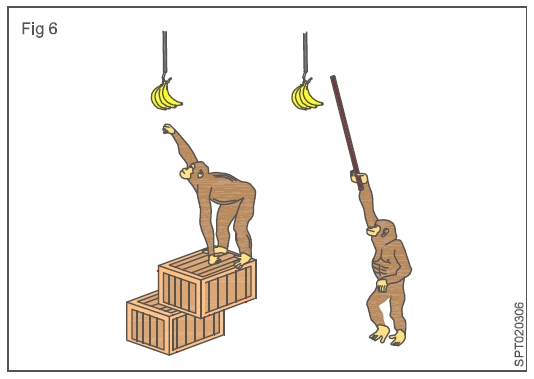
problems were the 'stick' problem and the ‘box’ problem both the problems involved
insightful solution
as shown in Figs 5 & 6

Two hollow bamboo
sticks, one long and the other short, were kept inside the cage. Since
the sticks were hollow, one stick could be pushed into one end
of the other to form a longer stick. However, if the two sticks are joined,
banana could be reached. First he tried with a short stick to
pull the bananas,
he failed. After fiddling
with the stick for sometime he realized that the
stick was too short to pull the bananas, the longer one would solve the problem
without fiddling. He tired with longer stick, through which he
got the banana
and ate it. The learner
acts according to the situation and
achieves success and in a similar situation next time they acts without
any problem because
of his past experience.